IMAP SMTP inbox access
MailSlurp mailboxes provide IMAP and SMTP access to your email accounts. This allows you to control inboxes using your favourite email client or using SMTP/IMAP libraries in any language you choose. Combine these techniques with the official SDK libraries and API endpoints to build powerful automations and tests.
Server endpoints
MailSlurp servers are found at the following locations:
| Protocol | Host | Port | Alt ports | TLS | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMTP | mxslurp.click | 2525 | 25 | false | SMTP server |
| SMTP | mailslurp.mx | 2465 | 587, 465, 2587 | true | SMTP server (secure) |
| IMAP | mailslurp.click | 1143 | - | false | IMAP server |
| IMAP | mailslurpimap.click | 8993 | 993 | true | IMAP server (secure) |
About
This article covers how to use IMAP and SMTP with MailSlurp inboxes. You can use these protocols to send and receive emails from your MailSlurp inboxes. To connect external inboxes instead see the inbox connectors feature. To use MailSlurp with mail clients like Outlook and Mail.app see the email clients guide.
SMTP vs IMAP
- SMTP is the outgoing mailserver for sending emails and
- IMAP is the incoming mailserver for reading emails.
You can use both protocols to interact with MailSlurp inboxes. The SMTP mail servers can also receive emails on your behalf.
Example projects
Here are some code samples hosted on GitHub:
Loading examples...
Authentication
You can authenticate IMAP and SMTP request as either an account or a specific inbox. Use
the getImapSmtpAccessDetails method to list access credentials or
view credentials in the dashboard. Credentials can either be account based
or inbox scoped. Use an inbox ID when fetching credentials to scope your access so that clients can only interact with
that inbox.
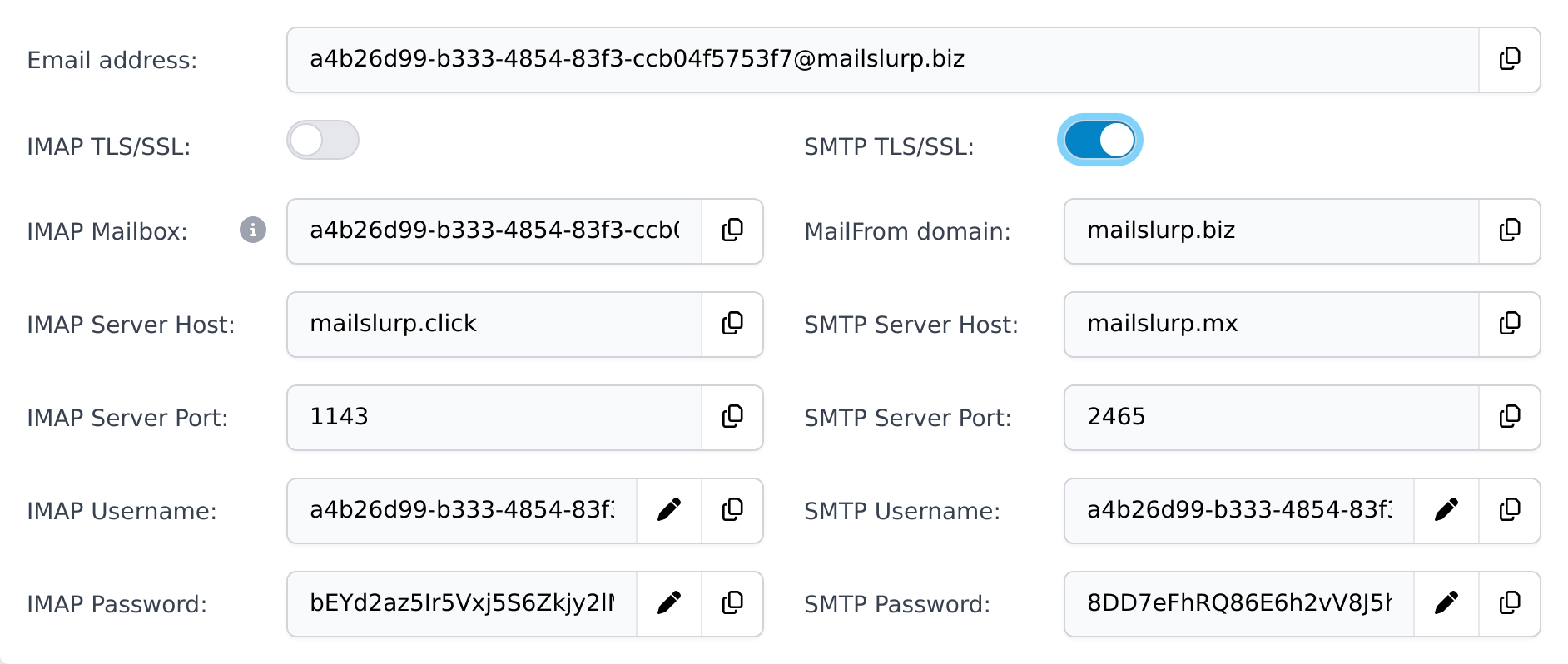
Access in the dashboard
You can find account-wide IMAP and SMTP access details on the MailSlurp dashboard homepage. Navigate to an inbox to get inbox scoped credentials.
Get access using SDK
You can use the SDK clients to obtain access details for mail servers. Then use these credentials to configure your IMAP and SMTP libraries.
Loading...
Use terminal and .env file
You can also fetch access details and store them in a .env file. These variables can be sourced during subsequent
IMAP/SMTP
calls.
- Bash
- Powershell
Loading...
TLS/SSL security
MailSlurp mailservers support TLS/SSL and STARTTLS using Let's Encrypt certificates issued by ACME. You may need to accept the authority when connecting to the server. Download the root CA certificates here and add them to your trust chain.
IMAP connections
Use IMAP to read emails from MailSlurp inboxes using an IMAP client library or mail program.
Get credentials
Locate the host and port of the IMAP server and the username and password. You can find the username like this:
Loading...
Get the password like so:
Loading...
Or visit the dashboard to view your credentials.
Command line access
Use curl in the command line to connect to MailSlurp inboxes using IMAP. Here are some examples:
- Insecure
- Secure
Loading...
Programmatic access
Use an IMAP client library for your programming language to connect to MailSlurp inboxes. Here are some examples:
- Javascript
Loading...
Mailbox selection
MailSlurp treats inboxes in your account like IMAP mailboxes. In account mode you can select INBOX to read all emails
in your account. In inbox mode you can select the inbox email address as the mailbox name.
UID and SeqNums
IMAP emails have unique identifiers (UIDs) and sequence numbers (SeqNums). Use these to fetch emails and mark them as read.
IMAP UIDs differ from email IDs in MailSlurp. Use IDs to fetch emails using the MailSlurp API and UIDs to fetch emails using IMAP.
IMAP usage
Here is an example using telnet and expect to read email via IMAP:
Loading...
IMAP commands
LOGIN
Login to as user and password:
Loading...
LIST
List mailboxes. Use INBOX to list all mailboxes in your account if using account mode access credentials.
Loading...
SELECT
Select a mailbox:
Loading...
SEARCH
Search for emails:
Loading...
FETCH
Fetch email content:
Loading...
STORE
Delete an email or mark it as read:
Loading...
SMTP connections
Use SMTP to send emails from MailSlurp inboxes using an SMTP client library.
Note: SMTP connection are only available on inboxes created with the
SMTP_INBOXtype.
Get credentials
You need to know the host and port of the SMTP server plus username and password. You can fetch the username like this:
Loading...
Get the password like so:
Loading...
Or visit the dashboard to view your credentials.
Authentication
MailSlurp SMTP servers support anonymous delivery and sending via AUTH PLAIN, and AUTH LOGIN mechanisms. When using AUTH PLAIN you must encode your username and password as base64 with \0 before each part. Here is an example:
Loading...
Command line access
Use command line tools to quickly send to or from SMTP mailboxes.
- Insecure
- Secure
Loading...
Programmatic access
Use an SMTP client library for your programming language to connect to MailSlurp inboxes. Here is an example using NodeJS and NodeMailer.
- Insecure
- Secure
Loading...
Creating an SMTP inbox
To access an inbox with SMTP you must create a new inbox using the SMTP_INBOX mailbox type. Once created you
will see a username and password for each protocol in the dashboard. You can also obtain
access credentials using the API.
import {CreateInboxDtoInboxTypeEnum, MailSlurp} from 'mailslurp-client';
const apiKey = process.env.API_KEY;
const mailslurp = new MailSlurp({apiKey});
// create an smtp inbox
const inboxSmtp = await mailslurp.inboxController.createInboxWithOptions({
createInboxDto: {
inboxType: CreateInboxDtoInboxTypeEnum.SMTP_INBOX,
}
});
SMTP usage
Here is a simple example using telnet and expect to send an email via SMTP:
Loading...
Sending emails
- Curl
Loading...
Delivering emails
You can submit emails to the SMTP mailservers to deliver them to inboxes. Use the MAIL FROM and RCPT TO commands to
specify the sender and recipient. You don't need authentication for this.
- Curl
- STARTTLS
- SMTPS
- SMTPS+SSL
Loading...
SMTP code examples
See the examples repository for more uses.
- Javascript
- Java
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
Loading...
Resources
For more information please see the following links:
